This blog compares two primary treatments for heart blockages: angioplasty and bypass surgery (CABG). It explains how each procedure works, when they are recommended, and the recovery process for both. Angioplasty is less invasive, with a faster recovery, while bypass surgery is more suitable for complex cases involving multiple blockages. The blog also outlines the potential risks, complications, and the long-term benefits of both options, helping patients make an informed decision about their heart health.
When it comes to treating heart problems, especially when arteries become blocked or narrowed, doctors may suggest two common procedures: angioplasty and bypass surgery. These procedures help restore blood flow to the heart, but they work in different ways. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between angioplasty and bypass surgery, also known as CABG surgery (Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting). We’ll also discuss the symptoms of heart failure after bypass surgery, recovery times, and when each procedure is recommended.
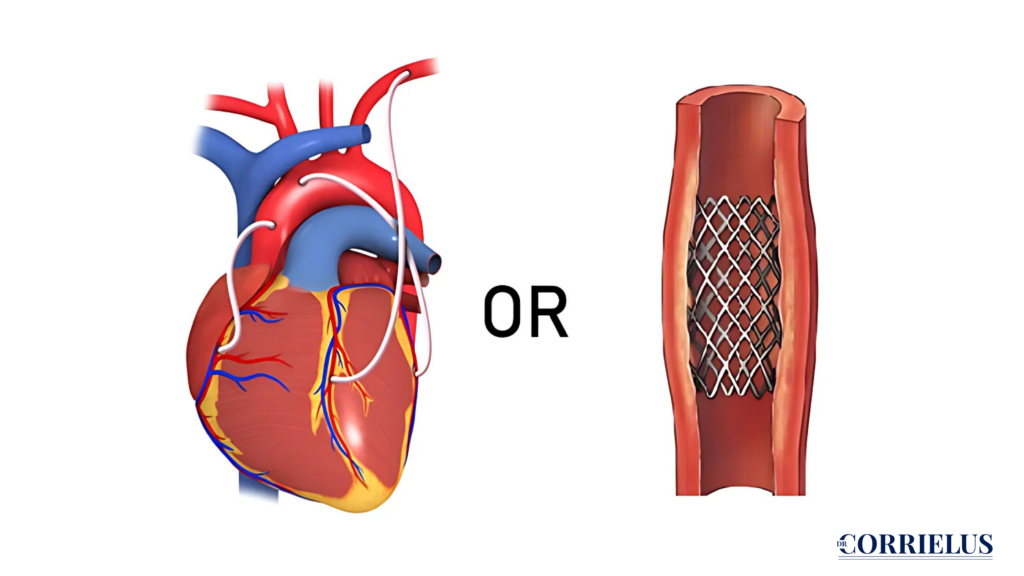
What is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is a procedure used to open blocked or narrowed arteries in the heart. The goal is to improve blood flow. It’s often used when there is a build-up of fatty deposits, known as plaque, inside the arteries. Angioplasty usually involves a small tube called a catheter, which is inserted into an artery. A balloon is attached to the catheter and inflated at the site of the blockage to help widen the artery. In some cases, a stent for heart blockage is placed to keep the artery open.
What is Bypass Surgery (CABG)?
CABG surgery, or coronary artery bypass graft surgery, is a more complex procedure. In this surgery, doctors take a healthy blood vessel from another part of your body and use it to create a new path (bypass) around the blocked arteries. The goal is to improve blood flow to the heart muscle. The CABG procedure is usually recommended when there are multiple blockages or when angioplasty isn’t an option.
When to Choose Angioplasty?
Angioplasty may be the right choice if:
- There is only one blockage in the heart.
- The blockage is in a location that’s easy to access.
- The artery is not severely damaged.
- You want a procedure that requires a shorter recovery time.
- You need a procedure that’s less invasive than bypass surgery.
When to Choose Bypass Surgery (CABG)?
CABG surgery may be the better option if:
- There are multiple blockages in your arteries.
- The blockage is in a main artery, like the left coronary artery.
- The arteries are severely damaged or hardened, making angioplasty difficult or ineffective.
- You have a history of heart attacks or other heart-related complications.
- Your heart function is weak, and you need a more long-term solution.
Key Differences Between Angioplasty and Bypass Surgery
Here’s a quick comparison of angioplasty and CABG surgery:
Feature | Angioplasty | CABG Surgery |
Invasiveness | Minimally invasive (small incision) | More invasive (open chest surgery) |
Recovery Time | Shorter (usually 1-2 weeks) | Longer (around 3 months) |
Suitable for | Single, less severe blockages | Multiple, severe blockages |
Effectiveness | Short-term solution | Long-term solution |
Risk of Complications | Lower risk | Higher risk due to surgery |
Angioplasty Procedure: Step-by-Step
The angioplasty procedure is typically done in a hospital setting. Here’s how it works:
- Preparation: You’ll be given a sedative and local anesthesia.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter (a long, flexible tube) is inserted into an artery, usually in your groin or wrist.
- Balloon Inflation: A small balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated at the site of the blockage.
- Stent Placement: If necessary, a stent for heart blockage is placed to keep the artery open.
- Procedure Completion: Once the balloon is deflated and removed, the catheter is also taken out, and you can recover.
CABG Procedure: Step-by-Step
The CABG procedure is more complex and involves these steps:
- Anesthesia: You’ll be given general anesthesia to sleep through the surgery.
- Incision: A surgeon will make a cut in your chest and spread the ribs to reach your heart.
- Bypass Creation: The surgeon takes a healthy blood vessel from your leg, chest, or arm and uses it to bypass the blocked coronary artery.
- Heart Restart: After the bypass is created, your heart is restarted.
- Recovery: You’ll be closely monitored in the hospital for several days.
Risks and Complications
Both angioplasty and bypass surgery carry risks. Here are some potential complications:
Risks of Angioplasty:
- Allergic reaction to contrast dye
- Heart attack or stroke
- Bleeding or infection at the insertion site
- Re-narrowing of the artery (in some cases)
Risks of CABG Surgery:
- Infection
- Symptoms of heart failure after bypass surgery, such as shortness of breath or fatigue
- Blood clots or bleeding
- Stroke
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
Angioplasty Recovery
Angioplasty recovery is quicker than bypass surgery. Most people go home the same day or after one night in the hospital. Within a week, many patients can return to their normal activities. However, it’s important to avoid strenuous activities for a few weeks to allow the artery to heal.
Heart Bypass Recovery
Heart bypass recovery is much longer. After the surgery, patients typically stay in the hospital for 5 to 7 days. Full recovery can take 2 to 3 months. During this time, it’s essential to rest and follow your doctor’s instructions for rehabilitation, including exercises and lifestyle changes.
Costs of Angioplasty vs. CABG Surgery
Both procedures are covered by insurance, but costs can vary widely depending on where you live and the complexity of the procedure. On average, angioplasty may cost between $10,000 to $30,000, while CABG surgery may cost between $40,000 and $150,000.
Symptoms of Heart Failure After Bypass Surgery
Some people may experience symptoms of heart failure after bypass surgery, including:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
- Difficulty sleeping due to breathlessness
- Reduced ability to exercise or do daily tasks
How to Choose Between Angioplasty and Bypass Surgery
The decision to have angioplasty or bypass surgery depends on various factors, such as:
- The severity and location of the blockage
- Your overall health and medical history
- Your doctor’s recommendation based on test results
- The risks and benefits of each procedure
A word from the Doctor —
Both angioplasty and CABG surgery have their advantages and risks. Angioplasty is less invasive, with a shorter recovery time, and works best for single or less severe blockages. CABG surgery, on the other hand, is a better choice for multiple blockages or more severe heart conditions. Talk to your doctor to determine which procedure is right for you, based on your individual heart health needs.
Your healthcare team will guide you through the options, helping you make the best decision for your heart health. Whether you choose angioplasty or CABG surgery, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and following your doctor’s advice will be key to long-term heart health.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Sanul Corrielus right away if you have questions about your heart health!